Traction Systems
A system which causes the propulsion of vehicle in which tractive or driving force is obtained from various devices such as diesel engine drives, steam engine drives, electric motors, etc. is called as traction system.
It can also be defined as the railway vehicle that provides the necessary traction power to move the train is referred as the traction or locomotive. This traction power can be diesel, steam or electric power.
The traction system can be classified as non-electric and electric traction systems.
1- Non-electric Traction System
A traction system that doesn’t use electrical energy for the movement of vehicle at any stage is referred as non-electric traction system.
The steam engine drive is the best example of a non electric traction system and it is the first locomotive system used before the invention of actual electric traction systems.

The steam locomotive system uses the superheated steam to produce mechanical energy for the movement of vehicle.
This may use coal or petroleum as fuel, liberates thermal energy to produce the steam pressure and then it is converted into kinetic energy so that mechanical movement of the vehicle is produced.
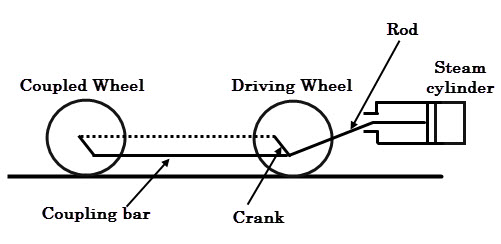
The disadvantages of steam locomotive systems , such as , low fuel efficiency, poor technical performance, maintenance of a large number of water supply facilities, and high maintenance cost makes them to be replaced by alternative traction systems and hence the electric traction.
The following are the two types of non electric traction systems.
- Steam engine drive based vehicles (used for railways)
- Internal combustion (IC) engine drive based vehicles (used for road transport)
- Maglev trains
2- Electric Traction System
Electric traction involves the use of electricity at some stage or all the stages of locomotive movement. This system includes straight electrical drive, diesel electric drive and battery operated electric drive vehicles.
In this, electrical motors are used for producing the vehicle movement and are powered by drawing electricity from utilities or diesel generators or batteries.

Advantages
- Cheapness. It is cheapest method of all other methods of traction.
- Cleanliness. It is free from smoke and flue gasses
- Maintenance cost. Maintenance and repair cost is about 50% of steam traction system.
- Starting time. It can be started without loss of time.
- High starting torque. This system uses of d.c. and a.c. series motors which has a very high starting torque.
- Braking. In electric traction , regenerative breaking is used which feeds back 40%of the energy.
- Saving in high grade coal. No coal is required for electric traction.
Disadvantages
- Higher initial expenditure.
- Failure of supply is a problem.
- Additional equipments are required for breaking purposes.
- The electrically operated vehicles have to move only on electrified track.
- Interference with telegraphs and telephone lines.
As mentioned above, electric traction systems can be self contained locomotives or vehicles that receive power from electric distribution system (substations). Self contained locomotives includes
- Battery operated electrical drives
- Diesel operated electrical drives
Vehicles that receives the power from substation is also referred as a third rail systems which includes
- Railway electric vehicles fed from overhead AC or DC supply
- Trolley buses or tramways supplied with DC supply (i.e., battery electric drives)
Traction Systems According to Efficiency
- Steam locomotive 5-7%
- Gas turbine electric locomotive 10%
- Diesel electric locomotive 26-30%
- Electric locomotive with thermal power plant 34-36%
- Electrical locomotive with Hydroelectric power plant 40-42%
Source: electronicshub.org; Dinesh Kumar Das
